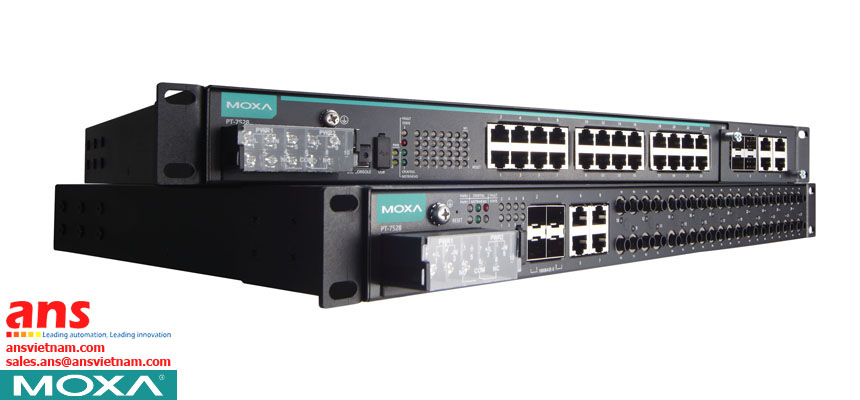
IEC 61850-3 PT-7528 Series Moxa vietnam
Xuất sứ: Moxa VietNam
Nhà cung cấp: Moxa VietNam ANS VietNam
Hãng sản xuất: Moxa
IEC 61850-3 PT-7528 Series Moxa vietnam
Features and Benefits
- Built-in MMS server based on IEC 61850-90-4 switch data modeling for Power SCADA
- Noise Guard™ wire speed zero packet loss technology
- Turbo Ring and Turbo Chain (recovery time < 20 ms @ 250 switches), RSTP/STP, and MSTP for network redundancy
- Isolated redundant power supplies with universal 24/48 VDC or 110/220 VDC/VAC power supply range
- -40 to 85°C operating temperature range
Introduction
The PowerTrans PT-7528 series is designed for power substation automation applications that operate in extremely harsh environments. The PT-7528 series supports Moxa’s new Noise Guard technology, is compliant with IEC 61850-3, and its EMC immunity exceeds IEEE 1613 Class 2 standards to ensure zero packet loss while transmitting at wire speed. The PT-7528 series also features critical packet prioritization (GOOSE, SMVs, and PTP), a built-in MMS server, and a configuration wizard designed specifically for substation automation. With Gigabit Ethernet, redundant ring, and 110/220 VDC/VAC isolated redundant power supplies, the PT-7528 series further increases the reliability of your communications and saves cabling/wiring costs. The wide range of PT-7528 models available support multiple types of port configuration, with up to 28 copper or fiber ports and 4 gigabit ports for uplink. Taken together, these features allow greater flexibility, making the PT-7528 suitable for a variety of industrial applications.
IEC 61850 Substation Solutions
 Maximizing a power substation’s availability and safety is the ultimate goal for both transmission grid operators and SAS (Substation Automation System) integrators. A properly optimized SAS ensures safe and continuous operation of substations. This brochure examines some key application scenarios that involve availability and safety, and considers the practical concerns electricity suppliers must account for when planning substation upgrades. In each case the focus is on how Moxa’s communication and computing solutions best minimize error probability, detect errors faster, and speed up fault corrections within the context of IEC 61850.......more
Maximizing a power substation’s availability and safety is the ultimate goal for both transmission grid operators and SAS (Substation Automation System) integrators. A properly optimized SAS ensures safe and continuous operation of substations. This brochure examines some key application scenarios that involve availability and safety, and considers the practical concerns electricity suppliers must account for when planning substation upgrades. In each case the focus is on how Moxa’s communication and computing solutions best minimize error probability, detect errors faster, and speed up fault corrections within the context of IEC 61850.......more
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Making Smart Substations Even Smarter: Enhancing Substation Reliability, Availability, and Maintainability
 This paper sketches out a few of the more important concerns that electricity suppliers should account for when planning substation upgrades. The focus is on how best to increase the reliability, availability, and maintainability of power substation automation networks within the context of the IEC 61850 vision, to give electricity suppliers a clear idea of the design procedures, device tolerances, and hardware and software features they should expect from the engineers and manufacturers who design and build their networking and computing devices.......more
This paper sketches out a few of the more important concerns that electricity suppliers should account for when planning substation upgrades. The focus is on how best to increase the reliability, availability, and maintainability of power substation automation networks within the context of the IEC 61850 vision, to give electricity suppliers a clear idea of the design procedures, device tolerances, and hardware and software features they should expect from the engineers and manufacturers who design and build their networking and computing devices.......more
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Using MMS and SNMP to Integrate IT Management for Substation Automation
 The devices that electrical substation automation systems are built from depend on highly precise, time-critical communications. Substation thus often use highly specialized monitoring systems to tackle this problem, but can approach it using different technologies. The most up-to-date, “smart” substations use the Manufacturing Messaging Specification (MMS) for communications among IEC 61850 intelligent electronic devices (IEDs), allowing SCADA to monitor and control IED states as well as process switchgear and transformer data directly. However, IT networking devices have been increasingly applied in IEC 61850 systems, and this equipment communicates using SNMP. Consequently, in the modern substation automation industry it’s clear that, for the time being, SNMP and MMS will continue to exist side-by-side. For designers and integrators of electrical substation equipment, bringing both MMS and SNMP support to IT equipment is an ideal, one-size fits-all alternative that allows for the greatest flexibility and adaptability around........more
The devices that electrical substation automation systems are built from depend on highly precise, time-critical communications. Substation thus often use highly specialized monitoring systems to tackle this problem, but can approach it using different technologies. The most up-to-date, “smart” substations use the Manufacturing Messaging Specification (MMS) for communications among IEC 61850 intelligent electronic devices (IEDs), allowing SCADA to monitor and control IED states as well as process switchgear and transformer data directly. However, IT networking devices have been increasingly applied in IEC 61850 systems, and this equipment communicates using SNMP. Consequently, in the modern substation automation industry it’s clear that, for the time being, SNMP and MMS will continue to exist side-by-side. For designers and integrators of electrical substation equipment, bringing both MMS and SNMP support to IT equipment is an ideal, one-size fits-all alternative that allows for the greatest flexibility and adaptability around........more
| • Technology | |
| Standards | IEEE 802.3 for 10BaseT IEEE 802.3u for 100BaseT(X) and 100BaseFX IEEE 802.3ab for 1000BaseT(X) IEEE 802.3z for 1000BaseX IEEE 802.3x for Flow Control IEEE 802.1D for Spanning Tree Protocol IEEE 802.1w for Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol IEEE 802.1s for Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol IEEE 802.1Q for VLAN Tagging IEEE 802.1p for Class of Service IEEE 802.1X for Authentication IEEE 802.3ad for Port Trunk with LACP |
| • Software Features | |
| Management | IPv4/IPv6, SNMPv1/v2c/v3, DHCP Server/ Client, BootP, TFTP, SMTP, RARP, RMON, HTTP, HTTPS, Telnet, DHCP Option 66/67/82, LLDP, Flow Control, Back Pressure, SNMP Inform, Port Mirror, Fiber Check, Syslog |
| Filter | IGMPv1/v2, GMRP, GVRP, 802.1Q VLAN, VLAN Unaware, Port-Based VLAN, GVRP |
| Redundancy Protocols | STP/RSTP, MSTP, Turbo Ring v1/v2, Turbo Chain, Link Aggregation |
| Security | RADIUS, TACACS+, SSL, SSH, Port Lock, Broadcast Storm Protection, Rate Limit |
| Time Management | SNTP, NTP Server/Client, IEEE 1588v2 PTP (software-based) |
| Industrial Protocols | EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP |
| MIB | MIB-II, Ethernet-like MIB, P-BRIDGE MIB, Q-BRIDGE MIB, Bridge MIB, RSTP MIB, RMON MIB Group 1, 2, 3, 9 |
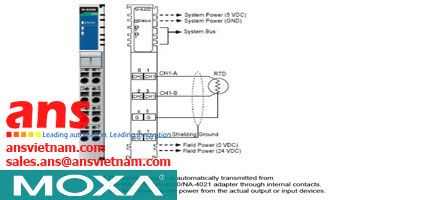
| Power Substation | MMS, IEC 61850 QoS, Configuration Wizard |
| • Switch Properties | |
| Priority Queues | 4 |
| Max. Number of VLANs | 256 |
| VLAN ID Range | VID 1 to 4094 |
| IGMP Groups | 256 |
| Jumbo Frame Size | 9728 bytes |
| • Interface | |
| RJ45 Ports | 10/100/1000BaseT(X) auto negotiation speed |
| Fiber Ports | 100/1000BaseSFP slot, 100BaseFX Multi-mode ST/SC Connector |
| Console Port | USB console port (Type B connector) |
| Storage Port | USB storage port (Type A connector) |
| Alarm Contact | 1 relay output with current carrying capacity of 3 A @ 30 VDC or 3 A @ 240 VAC |
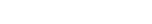
| • Optical Fiber | |
 | |
| • Power Requirements | |
| Input Voltage | • WV: 24/48 VDC • HV: 110/220 VDC/VAC |
| Operating Voltage | • WV: 18 to 72 V • HV: 88 to 300 VDC and 85 to 264 VAC |
| Input Current | For models with fewer than 8 fiber ports: • Max. 0.741 A @ 24 VDC • Max. 0.364 A @ 48 VDC • Max. 0.147/0.077 A @ 110/220 VDC • Max. 0.283/0.19 A @ 110/220 VAC For models with 8 or more fiber ports: • Max. 1.428 A @ 24 VDC • Max. 0.735 A @ 48 VDC • Max. 0.313/0.167 A @ 110/220 VDC • Max. 0.586/0.382 A @ 110/220 VAC |
| Overload Current Protection | Present |
| Connection | 10-pin terminal block |
| Reverse Polarity Protection | Present |
| • Physical Characteristics | |
| Housing | Aluminum alloy |
| IP Rating | IP40 protection |
| Dimensions | 440 x 44 x 325 mm (17.32 x 1.73 x 12.80 in) |
| Weight | 4900 g (10.89 lb) |
| Installation | 19-inch rack mounting |
| • Environmental Limits | |
| Operating Temperature | -40 to 85°C (-40 to 185°F), cold start requires min. of 100 VAC at -40°C |
| Storage Temperature | -40 to 85°C (-40 to 185°F) |
| Ambient Relative Humidity | 5 to 95% (non-condensing) |
| • Standards and Certifications | |
| Safety | UL 508 |
| EMI | FCC Part 15 Subpart B Class A, EN 55032 Class A |
| EMS | IEC 61000-4-2 ESD: Contact: 8 kV; Air: 15 kV IEC 61000-4-3 RS: 80 MHz to 1 GHz: 35 V/m IEC 61000-4-4 EFT: Power: 4 kV; Signal: 4 kV IEC 61000-4-5 Surge: Power: 4 kV; Signal: 4 kV IEC 61000-4-6 CS: 10 V IEC 61000-4-8 IEC 61000-4-11 |
| Rail Traffic | EN 50121-4 |
| Transportation | NEMA TS2 |
| Electrical Substation | IE C61850-3, IEEE 1613 Class 2 (models with MCS and SSC fiber ports are compliant with IEEE 1613 Class 1) |
| • MTBF (mean time between failures) | |
| Time | 422,912 hrs |
| Standard | Telcordia TR/SR |
| • Warranty | |
| Warranty Period | 5 years |
| Details | www.anhnghison.com |



























































































































































































































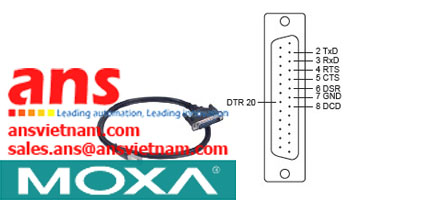






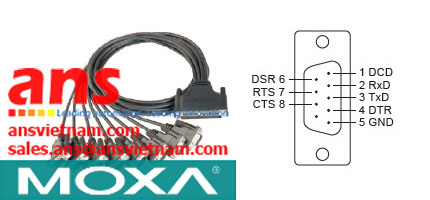





















































































































































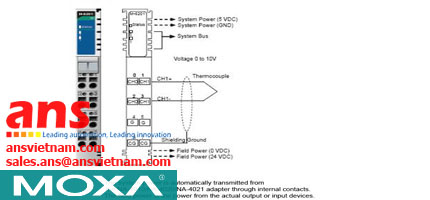














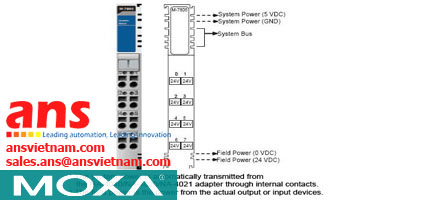

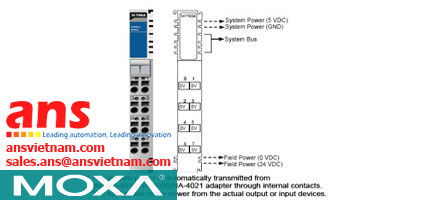

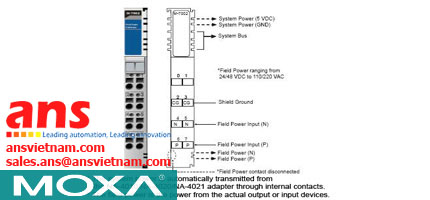
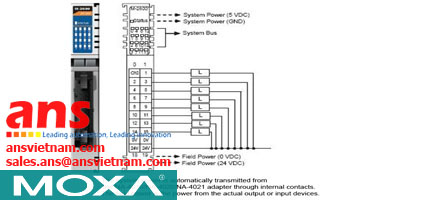
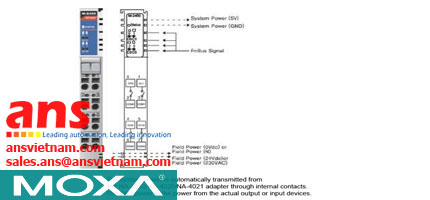
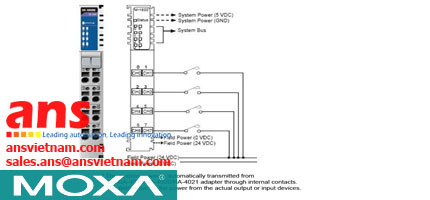

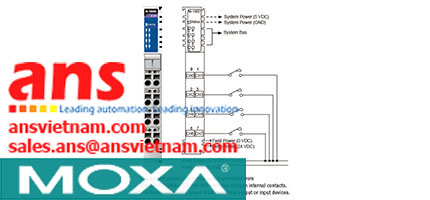






























































































































































































































































































![Cables-CBL-M12[FF5P]-OPEN-100-IP67-Moxa-vietnam.jpg](/Images/products/thumb/Cables-CBL-M12[FF5P]-OPEN-100-IP67-Moxa-vietnam.jpg)